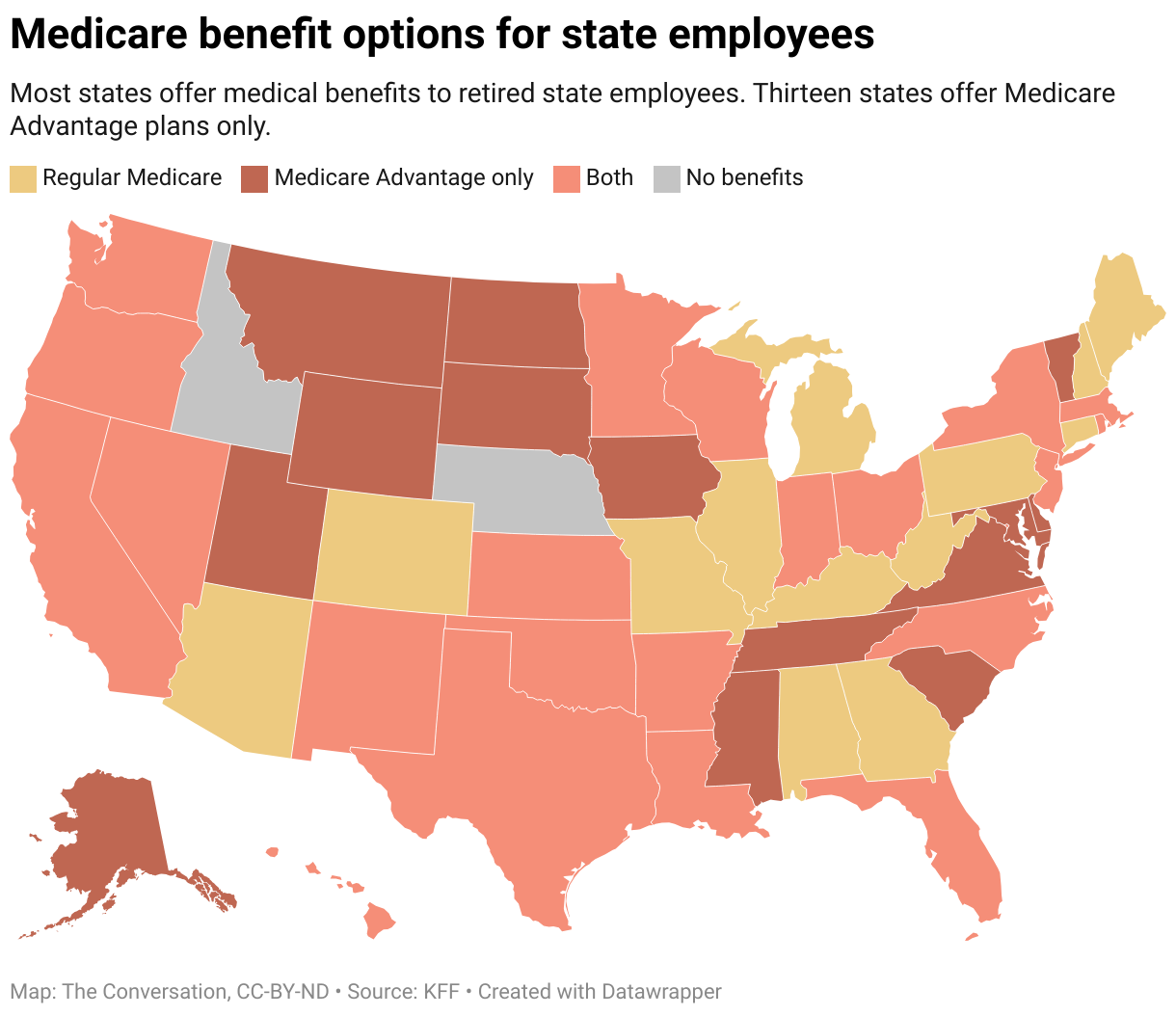
Key Events
Over five decades since 1972, Americans got more health insurance from public sources and less from private companies, while the number of uninsured citizens rose and fell. The ten key events below shaped America’s health insurance landscape and continue to inform today’s policy debates.
1972

Premiums rise nearly 14%. Social Security allows people under 65 with long-term disabilities to join Medicare, expanding its ranks.
1982

President Reagan signs the Tax Equity and Fiscal Responsibility Act, adding a hospice benefit to Medicare.
1986
The Emergency Medical Treatment and Labor Act requires hospitals to offer emergency treatment. Medicaid covers pregnant women up to 100% of the poverty level.
1993

President Clinton’s Health Securities Act fails to pass Congress.
1996

HIPAA limits insurance companies from excluding people with pre-existing conditions.
1997

State Children’s Health Insurance Program covers low-income children. Medicare expanded to include Medicare Advantage.
2003

Health Savings Accounts are born, providing tax advantages for spending on medical expenses.
2006

President Bush signs landmark Medicare reform bill including a new Part D drug benefit.
2010
Uninsured population peaks. President Obama signs Affordable Care Act, expanding Medicaid and creating a federal insurance exchange.
2016
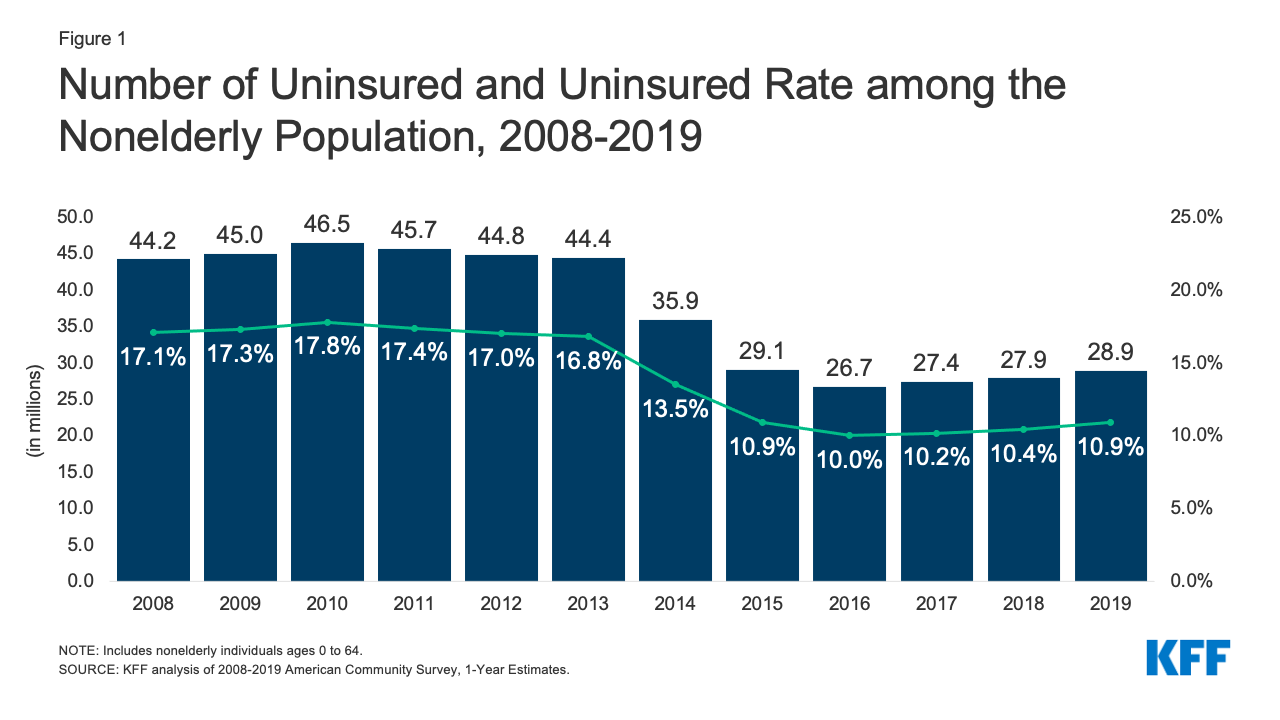
America’s uninsured population drops by 20 million to an historic low. ACA plans lift the individual private insurance market.
Methodology
Estimates for all groups except for Medicare are based on the National Health Interview Survey and represent long-term trends in the number and percentage of persons under age 65 years with different types of health insurance coverage and with no coverage.
Estimates for Medicare are from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services and include both persons over and under age 65 with Medicare.
Individual (nongroup) coverage includes persons covered by private insurance purchased directly as well as plans obtained through school or other means. Beginning in 2014, this category also includes plans purchased through the Health Insurance Marketplace or a state-based exchange.
Military coverage includes TRICARE (CHAMPUS), CHAMP-VA, and VA coverage. From 1997–2007 it also includes a small number of other government programs.
Percentage figures represent relationships between the observed groups and may differ from the groups’ percentages of the total U.S. adult population.
Timeline sources:
Medicare and Medicaid Milestones
Private Health Insurance in 1973: A Review of Coverage, Enrollment, and Financial Experience
Timeline: History of Health Reform in the U.S.